Masters project: Condensation in porous media: a fractal analysis of avalanches
Context
This post documents my masters thesis, completed in May 2022, under the supervision of Dr Sergei Taraskin. The subject of the paper is the disorder-induced phase transition that occurs in a lattice-gas model of condensation within a highly porous, disordered substrate such as aerogel. I like to call the model the ‘porous lattice gas model’, but its creators, Kierlik, Rosinberg, Tarjus, and Pitard 1, did not use that name.
The paper itself is attached as a pdf below, and I have reproduced the abstract for this webpage. Meanwhile, all the code is available on my GitHub, and there is an example listing from the main numerical module below.
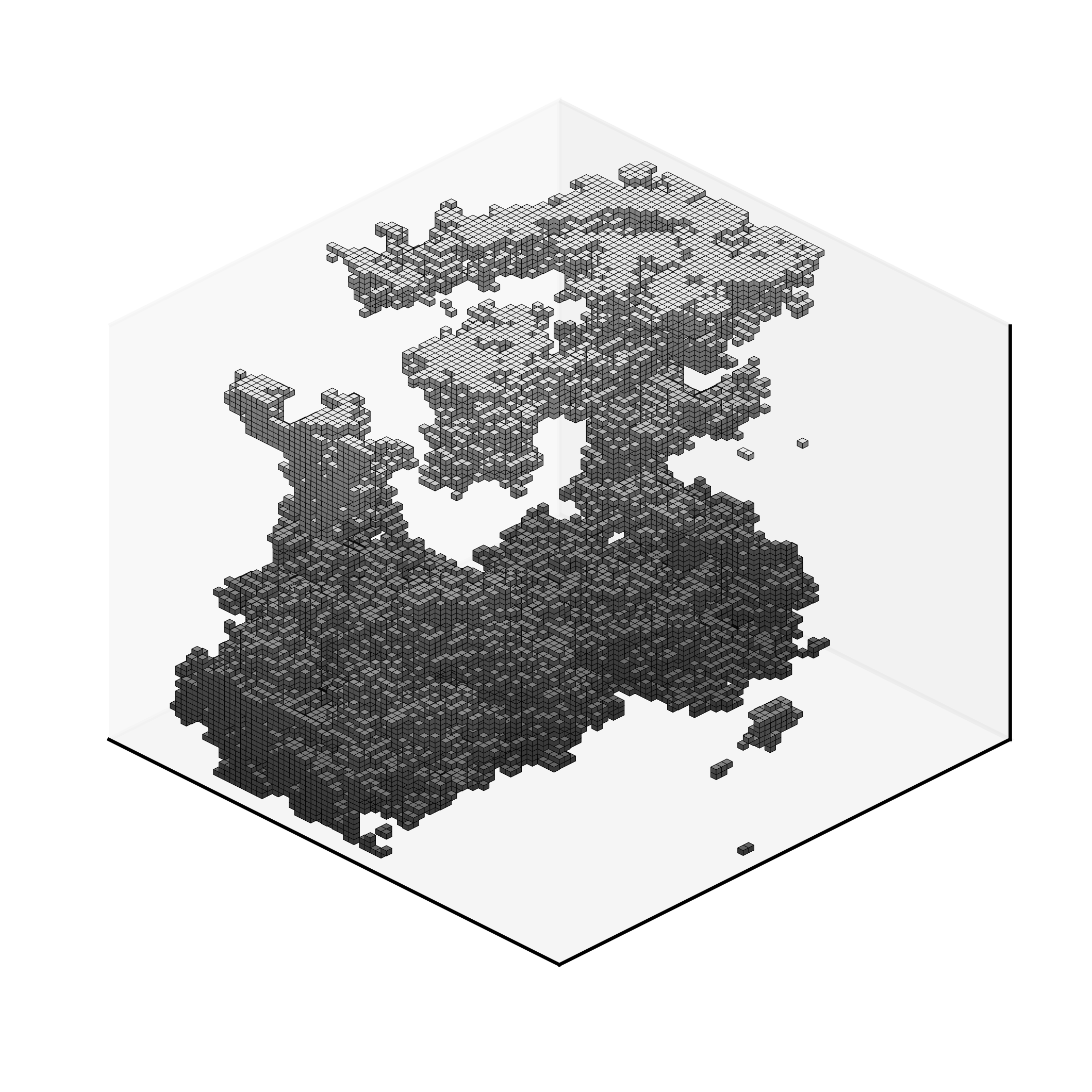
Abstract
The random-field Ising model is the archetypical system for modelling phase transitions in disordered systems, and it provided the first example of a disorder-induced critical point. More recently, analogous critical behaviour has been discovered in the porous lattice gas model of condensation in a disordered medium. It is an open question whether these two critical points are in the same universality class, as is the case for the conventional 3-dimensional Ising model and the liquid-gas transition. Here, we investigate this possibility by calculating the fractal dimensions of the so-called spanning avalanches that occur in the porous lattice gas transition; these dimensions are universal exponents. We estimate that the volumetric fractal dimension of one type of spanning avalanche, known as subcritical 3-dimensional, is 0.971 ± 003, in contradiction with previous estimates from the random-field Ising model, of 0.993 ± 007. There remain, however, doubts about the validity of this number.
Download PDF
Program module with the key numerical routines for sandbox analysis
! Filename: sandbox.f95
! Core code to perform sandbox analysis on a single avalanche. To be called by
! program main stored in main.f95
module sandbox
implicit none
contains
subroutine main_loop(coords, A, T, mp, vp, mf, vf)
integer, intent(in) :: &
coords(:,:), & ! BCC coordinates of avalanche fluid cells
A(:,:,:), & ! Array representation of avalanche
T(:,:,:) ! Array representation of pore space
real*8, intent(out) :: &
mp(:), & ! Mean number of pore cells in bounding box of linear size
! [index]
vp(:), & ! As above, but variance
mf(:), & ! Mean number of fluid cells in bounding box of linear
! size [index]
vf(:) ! As above, but variance
integer, allocatable :: tessA(:,:,:), tessT(:,:,:), ii(:,:,:), iiT(:,:,:)
integer :: x, y, z, coord(3), lmax, l
integer*8 :: n, numsites, f, p
! Get important sizes from arguments
numsites = size(coords, 1)
lmax = size(A, 1)
! [1, lmax]^3 references the centre of the tesselated system
allocate(tessA(-lmax+1 : 2*lmax, -lmax+1 : 2*lmax, -lmax+1 : 2*lmax), &
tessT(-lmax+1 : 2*lmax, -lmax+1 : 2*lmax, -lmax+1 : 2*lmax), &
ii(-lmax : 2*lmax, -lmax : 2*lmax, -lmax : 2*lmax), &
iiT(-lmax : 2*lmax, -lmax : 2*lmax, -lmax : 2*lmax))
! One greater on each dimension to prevent OOB
! Tesselate A 3x3x3 times to deal with periodic BCs. Then, make
! integral image from it
do x = -lmax + 1, lmax + 1, lmax
do y = -lmax + 1, lmax + 1, lmax
do z = -lmax + 1, lmax + 1, lmax
tessA(x : x+lmax-1, y : y+lmax-1, z : z+lmax-1) = A
tessT(x : x+lmax-1, y : y+lmax-1, z : z+lmax-1) = T
end do
end do
end do
call makeii(lmax, tessA, ii)
call makeii(lmax, tessT, iiT)
! Calculate total mass in system
mp = 0.; vp = 0.; mf = 0.; vf = 0.
# ifdef DEBUG
write(*, "(a8, i8, 5a4)") 'origin /', numsites, 'x', 'y', 'z', 'l'
# endif
! Main loop
do n = 1, numsites
coord = coords(n, :)
! Can save effort for single-element boxes
f = A(coord(1), coord(2), coord(3))
p = T(coord(1), coord(2), coord(3))
call iterate_stats(n, mf(1), vf(1), f)
call iterate_stats(n, mp(1), vp(1), p)
do l = 2, lmax
#ifdef DEBUG
write(*, '(a, i16, 5i4)', advance='no') achar(13), n, coord, l
#endif
call iisum(lmax, l, ii, coord, f)
call iisum(lmax, l, iiT, coord, p)
call iterate_stats(n, mf(l), vf(l), f)
call iterate_stats(n, mp(l), vp(l), p)
end do
end do
! E(x^2) - (E(x))^2
vp = vp - mp**2
vf = vf - mf**2
# ifdef DEBUG
write(*,*)
# endif
end subroutine main_loop
subroutine makeii(D, A, ii)
! Construct the integral image (Viola, Jones 2004) from a given array.
! Had to make the argument list a bit ugly to retain funky subscripts
integer, intent(in) :: D ! 1/3 * sidelength of A
! Array ('image') we wish to compute sums on
integer, intent(in), dimension(-D+1:2*D, -D+1:2*D, -D+1:2*D) :: A
! Output object for integral image
integer, intent(out),dimension(-D:2*D, -D:2*D, -D:2*D) :: ii
integer :: x, y, z
ii = 0
do x = -D + 1, 2*D ! Recall ii has non-standard subscripts
do y = -D + 1, 2*D
do z = -D + 1, 2*D
ii(x, y, z) = A(x, y, z) &
+ ii(x-1, y, z) + ii(x, y-1, z) + ii(x, y, z-1) &
- ii(x-1, y-1, z) - ii(x-1, y, z-1) - ii(x, y-1, z-1) &
+ ii(x-1, y-1, z-1)
end do
end do
end do
end subroutine makeii
subroutine iisum(lmax, l, ii, centre, mass)
! Compute a box sum on an array by utilising the integral image
! representation. This method performs independently of box size.
integer, intent(in) :: lmax
! The integral image array
integer, dimension(-lmax:2*lmax,-lmax:2*lmax,-lmax:2*lmax), intent(in) :: ii
integer, intent(in) :: l ! Sidelength of box to sum
integer, intent(in) :: centre(3) ! Centre of box
integer*8, intent(out) :: mass ! Where the total will be put
integer :: lb(3)
if (mod(l, 2) == 0) then ! Test even
lb = centre - (l/2 - 1) - 1 ! Asymmetric bounds
else
lb = centre - (l - 1)/2 - 1 ! Symmetric bounds
end if
! Can be expressed more succintly but this needs to go fast
mass = ii(lb(1) + l, lb(2) + l, lb(3) + l) &
- ii(lb(1) + l, lb(2) + l, lb(3) ) &
- ii(lb(1) + l, lb(2) , lb(3) + l) &
- ii(lb(1) , lb(2) + l, lb(3) + l) &
+ ii(lb(1) + l, lb(2) , lb(3) ) &
+ ii(lb(1) , lb(2) + l, lb(3) ) &
+ ii(lb(1) , lb(2) , lb(3) + l) &
- ii(lb(1) , lb(2) , lb(3) )
end subroutine iisum
subroutine iterate_stats(n, mean, sumsq, datum)
! Update mean and sum of squares using 'datum' when moving from n - 1 to n
! data points. i.e. this should first be called with n=1.
integer*8, intent(in) :: n
integer*8, intent(in) :: datum
real*8, intent(inout) :: mean, sumsq
mean = (datum + (n - 1)*mean) / n
sumsq = (datum**2 + (n - 1)*sumsq) / n
end subroutine iterate_stats
end module sandbox
References
A word on copyright
Unless otherwise stated, all written material, images, and code on this webpage and in the paper are entirely my own work. If you wish to reuse anything, I would kindly request that you clearly credit myself and Dr Taraskin.
-
Kierlik, E., Rosinberg, M. L., Tarjus, G. & Pitard, E. Molecular Physics 95, 341–351. (1998). ↩